doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9502
Preview meta tags from the doi.org website.
Linked Hostnames
34- 180 links todoi.org
- 54 links toscholar.google.com
- 34 links toadsabs.harvard.edu
- 23 links towww.nature.com
- 10 links toscholar.google.co.uk
- 10 links towww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- 8 links tolink.springer.com
- 7 links towww.springernature.com
Thumbnail
Search Engine Appearance
Identifying causal gateways and mediators in complex spatio-temporal systems - Nature Communications
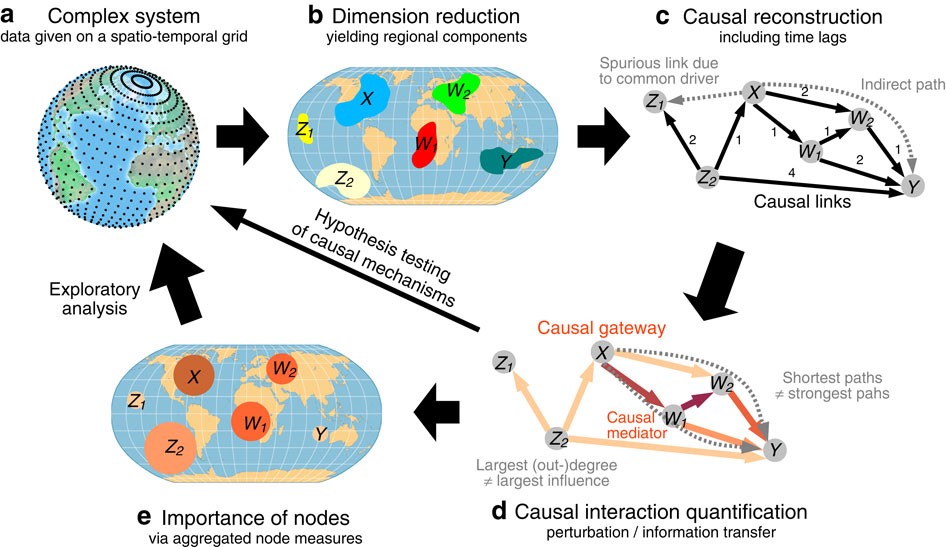
Identifying regions important for spreading and mediating perturbations is crucial to assess the susceptibilities of spatio-temporal complex systems such as the Earth’s climate to volcanic eruptions, extreme events or geoengineering. Here a data-driven approach is introduced based on a dimension reduction, causal reconstruction, and novel network measures based on causal effect theory that go beyond standard complex network tools by distinguishing direct from indirect pathways. Applied to a data set of atmospheric dynamics, the method identifies several strongly uplifting regions acting as major gateways of perturbations spreading in the atmosphere. Additionally, the method provides a stricter statistical approach to pathways of atmospheric teleconnections, yielding insights into the Pacific–Indian Ocean interaction relevant for monsoonal dynamics. Also for neuroscience or power grids, the novel causal interaction perspective provides a complementary approach to simulations or experiments for understanding the functioning of complex spatio-temporal systems with potential applications in increasing their resilience to shocks or extreme events. Identifying regions important for spreading and mediating perturbations is crucial to assess the susceptibilities of complex systems such as the Earth’s climate. Here the authors introduce a data-driven approach that identifies causal pathways, and apply it to a global atmospheric data set.
Bing
Identifying causal gateways and mediators in complex spatio-temporal systems - Nature Communications
Identifying regions important for spreading and mediating perturbations is crucial to assess the susceptibilities of spatio-temporal complex systems such as the Earth’s climate to volcanic eruptions, extreme events or geoengineering. Here a data-driven approach is introduced based on a dimension reduction, causal reconstruction, and novel network measures based on causal effect theory that go beyond standard complex network tools by distinguishing direct from indirect pathways. Applied to a data set of atmospheric dynamics, the method identifies several strongly uplifting regions acting as major gateways of perturbations spreading in the atmosphere. Additionally, the method provides a stricter statistical approach to pathways of atmospheric teleconnections, yielding insights into the Pacific–Indian Ocean interaction relevant for monsoonal dynamics. Also for neuroscience or power grids, the novel causal interaction perspective provides a complementary approach to simulations or experiments for understanding the functioning of complex spatio-temporal systems with potential applications in increasing their resilience to shocks or extreme events. Identifying regions important for spreading and mediating perturbations is crucial to assess the susceptibilities of complex systems such as the Earth’s climate. Here the authors introduce a data-driven approach that identifies causal pathways, and apply it to a global atmospheric data set.
DuckDuckGo
Identifying causal gateways and mediators in complex spatio-temporal systems - Nature Communications
Identifying regions important for spreading and mediating perturbations is crucial to assess the susceptibilities of spatio-temporal complex systems such as the Earth’s climate to volcanic eruptions, extreme events or geoengineering. Here a data-driven approach is introduced based on a dimension reduction, causal reconstruction, and novel network measures based on causal effect theory that go beyond standard complex network tools by distinguishing direct from indirect pathways. Applied to a data set of atmospheric dynamics, the method identifies several strongly uplifting regions acting as major gateways of perturbations spreading in the atmosphere. Additionally, the method provides a stricter statistical approach to pathways of atmospheric teleconnections, yielding insights into the Pacific–Indian Ocean interaction relevant for monsoonal dynamics. Also for neuroscience or power grids, the novel causal interaction perspective provides a complementary approach to simulations or experiments for understanding the functioning of complex spatio-temporal systems with potential applications in increasing their resilience to shocks or extreme events. Identifying regions important for spreading and mediating perturbations is crucial to assess the susceptibilities of complex systems such as the Earth’s climate. Here the authors introduce a data-driven approach that identifies causal pathways, and apply it to a global atmospheric data set.
General Meta Tags
164- titleIdentifying causal gateways and mediators in complex spatio-temporal systems | Nature Communications
- titleClose banner
- titleClose banner
- X-UA-CompatibleIE=edge
- applicable-devicepc,mobile
Open Graph Meta Tags
6- og:urlhttps://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms9502
- og:typearticle
- og:site_nameNature
- og:titleIdentifying causal gateways and mediators in complex spatio-temporal systems - Nature Communications
- og:descriptionIdentifying regions important for spreading and mediating perturbations is crucial to assess the susceptibilities of complex systems such as the Earth’s climate. Here the authors introduce a data-driven approach that identifies causal pathways, and apply it to a global atmospheric data set.
Twitter Meta Tags
6- twitter:site@NatureComms
- twitter:cardsummary_large_image
- twitter:image:altContent cover image
- twitter:titleIdentifying causal gateways and mediators in complex spatio-temporal systems
- twitter:descriptionNature Communications - Identifying regions important for spreading and mediating perturbations is crucial to assess the susceptibilities of complex systems such as the Earth’s climate. Here...
Item Prop Meta Tags
5- position1
- position2
- position3
- position4
- publisherSpringer Nature
Link Tags
15- alternatehttps://www.nature.com/ncomms.rss
- apple-touch-icon/static/images/favicons/nature/apple-touch-icon-f39cb19454.png
- canonicalhttps://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms9502
- icon/static/images/favicons/nature/favicon-48x48-b52890008c.png
- icon/static/images/favicons/nature/favicon-32x32-3fe59ece92.png
Emails
1Links
363- http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-data_query?link_type=ABSTRACT&bibcode=1981MWRv..109..784W
- http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-data_query?link_type=ABSTRACT&bibcode=1989PhyD...35..395V
- http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-data_query?link_type=ABSTRACT&bibcode=1991JAtS...48..752G
- http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-data_query?link_type=ABSTRACT&bibcode=1993ClCh...25..179B
- http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-data_query?link_type=ABSTRACT&bibcode=1996BAMS...77..437K