doi.org/10.1038/s41370-018-0104-3
Preview meta tags from the doi.org website.
Linked Hostnames
35- 105 links todoi.org
- 26 links towww.nature.com
- 17 links toscholar.google.com
- 7 links toscholar.google.co.uk
- 7 links towww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- 7 links towww.springernature.com
- 4 links topartnerships.nature.com
- 3 links toauthorservices.springernature.com
Thumbnail
Search Engine Appearance
Exposure to selected preservatives in personal care products: case study comparison of exposure models and observational biomonitoring data - Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology
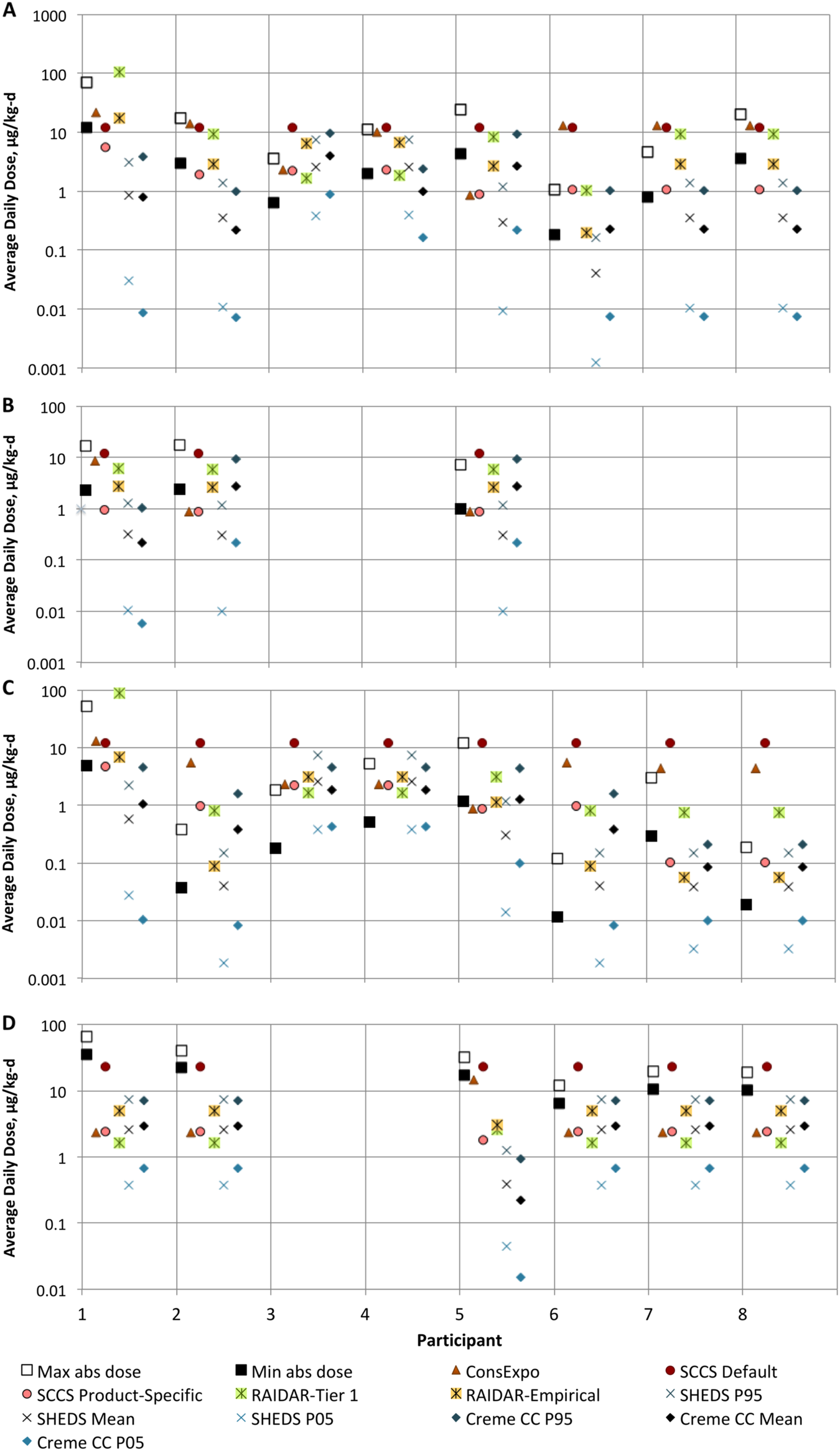
Exposure models provide critical information for risk assessment of personal care product ingredients, but there have been limited opportunities to compare exposure model predictions to observational exposure data. Urinary excretion data from a biomonitoring study in eight individuals were used to estimate minimum absorbed doses for triclosan and methyl-, ethyl-, and n-propyl- parabens (TCS, MP, EP, PP). Three screening exposure models (European Commission Scientific Commission on Consumer Safety [SCCS] algorithms, ConsExpo in deterministic mode, and RAIDAR-ICE) and two higher-tier probabilistic models (SHEDS-HT, and Creme Care & Cosmetics) were used to model participant exposures. Average urinary excretion rates of TCS, MP, EP, and PP for participants using products with those ingredients were 16.9, 3.32, 1.9, and 0.91 μg/kg-d, respectively. The SCCS default aggregate and RAIDAR-ICE screening models generally resulted in the highest predictions compared to other models. Approximately 60–90% of the model predictions for most of the models were within a factor of 10 of the observed exposures; ~30–40% of the predictions were within a factor of 3. Estimated exposures from urinary data tended to fall in the upper range of predictions from the probabilistic models. This analysis indicates that currently available exposure models provide estimates that are generally realistic. Uncertainties in preservative product concentrations and dermal absorption parameters as well as degree of metabolism following dermal absorption influence interpretation of the modeled vs. measured exposures. Use of multiple models may help characterize potential exposures more fully than reliance on a single model.
Bing
Exposure to selected preservatives in personal care products: case study comparison of exposure models and observational biomonitoring data - Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology
Exposure models provide critical information for risk assessment of personal care product ingredients, but there have been limited opportunities to compare exposure model predictions to observational exposure data. Urinary excretion data from a biomonitoring study in eight individuals were used to estimate minimum absorbed doses for triclosan and methyl-, ethyl-, and n-propyl- parabens (TCS, MP, EP, PP). Three screening exposure models (European Commission Scientific Commission on Consumer Safety [SCCS] algorithms, ConsExpo in deterministic mode, and RAIDAR-ICE) and two higher-tier probabilistic models (SHEDS-HT, and Creme Care & Cosmetics) were used to model participant exposures. Average urinary excretion rates of TCS, MP, EP, and PP for participants using products with those ingredients were 16.9, 3.32, 1.9, and 0.91 μg/kg-d, respectively. The SCCS default aggregate and RAIDAR-ICE screening models generally resulted in the highest predictions compared to other models. Approximately 60–90% of the model predictions for most of the models were within a factor of 10 of the observed exposures; ~30–40% of the predictions were within a factor of 3. Estimated exposures from urinary data tended to fall in the upper range of predictions from the probabilistic models. This analysis indicates that currently available exposure models provide estimates that are generally realistic. Uncertainties in preservative product concentrations and dermal absorption parameters as well as degree of metabolism following dermal absorption influence interpretation of the modeled vs. measured exposures. Use of multiple models may help characterize potential exposures more fully than reliance on a single model.
DuckDuckGo
Exposure to selected preservatives in personal care products: case study comparison of exposure models and observational biomonitoring data - Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology
Exposure models provide critical information for risk assessment of personal care product ingredients, but there have been limited opportunities to compare exposure model predictions to observational exposure data. Urinary excretion data from a biomonitoring study in eight individuals were used to estimate minimum absorbed doses for triclosan and methyl-, ethyl-, and n-propyl- parabens (TCS, MP, EP, PP). Three screening exposure models (European Commission Scientific Commission on Consumer Safety [SCCS] algorithms, ConsExpo in deterministic mode, and RAIDAR-ICE) and two higher-tier probabilistic models (SHEDS-HT, and Creme Care & Cosmetics) were used to model participant exposures. Average urinary excretion rates of TCS, MP, EP, and PP for participants using products with those ingredients were 16.9, 3.32, 1.9, and 0.91 μg/kg-d, respectively. The SCCS default aggregate and RAIDAR-ICE screening models generally resulted in the highest predictions compared to other models. Approximately 60–90% of the model predictions for most of the models were within a factor of 10 of the observed exposures; ~30–40% of the predictions were within a factor of 3. Estimated exposures from urinary data tended to fall in the upper range of predictions from the probabilistic models. This analysis indicates that currently available exposure models provide estimates that are generally realistic. Uncertainties in preservative product concentrations and dermal absorption parameters as well as degree of metabolism following dermal absorption influence interpretation of the modeled vs. measured exposures. Use of multiple models may help characterize potential exposures more fully than reliance on a single model.
General Meta Tags
106- titleExposure to selected preservatives in personal care products: case study comparison of exposure models and observational biomonitoring data | Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology
- X-UA-CompatibleIE=edge
- applicable-devicepc,mobile
- viewportwidth=device-width,initial-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=5,user-scalable=yes
- 360-site-verification5a2dc4ab3fcb9b0393241ffbbb490480
Open Graph Meta Tags
5- og:urlhttps://www.nature.com/articles/s41370-018-0104-3
- og:typearticle
- og:site_nameNature
- og:titleExposure to selected preservatives in personal care products: case study comparison of exposure models and observational biomonitoring data - Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology
- og:imagehttps://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41370-018-0104-3/MediaObjects/41370_2018_104_Fig1_HTML.png
Twitter Meta Tags
6- twitter:site@JExpSciEnvEpi
- twitter:cardsummary_large_image
- twitter:image:altContent cover image
- twitter:titleExposure to selected preservatives in personal care products: case study comparison of exposure models and observational biomonitoring data
- twitter:descriptionJournal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology - Exposure to selected preservatives in personal care products: case study comparison of exposure models and observational biomonitoring...
Item Prop Meta Tags
5- position1
- position2
- position3
- position4
- publisherSpringer Nature
Link Tags
15- alternatehttps://www.nature.com/jes.rss
- apple-touch-icon/static/images/favicons/nature/apple-touch-icon-f39cb19454.png
- canonicalhttps://www.nature.com/articles/s41370-018-0104-3
- icon/static/images/favicons/nature/favicon-48x48-b52890008c.png
- icon/static/images/favicons/nature/favicon-32x32-3fe59ece92.png
Emails
1Links
205- http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/43370/1/9241563117_eng.pdf
- http://cefic-lri.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/B7_Final-report.pdf
- http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
- http://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_risk/committees/04_sccp/docs/sccp_o_166.pdf
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=Dermal%20permeation%20data%20and%20models%20for%20the%20prioritization%20and%20screening-level%20exposure%20assessment%20of%20organic%20chemicals&journal=Environ%20Int&doi=10.1016%2Fj.envint.2016.05.025&volume=94&pages=424-35&publication_year=2016&author=Brown%2CTN&author=Armitage%2CJM&author=Egeghy%2CP&author=Kircanski%2CI&author=Arnot%2CJA