www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0600/acute-monoarthritis.html
Preview meta tags from the www.aafp.org website.
Linked Hostnames
1Thumbnail
Search Engine Appearance
Acute Monoarthritis: Diagnosis in Adults
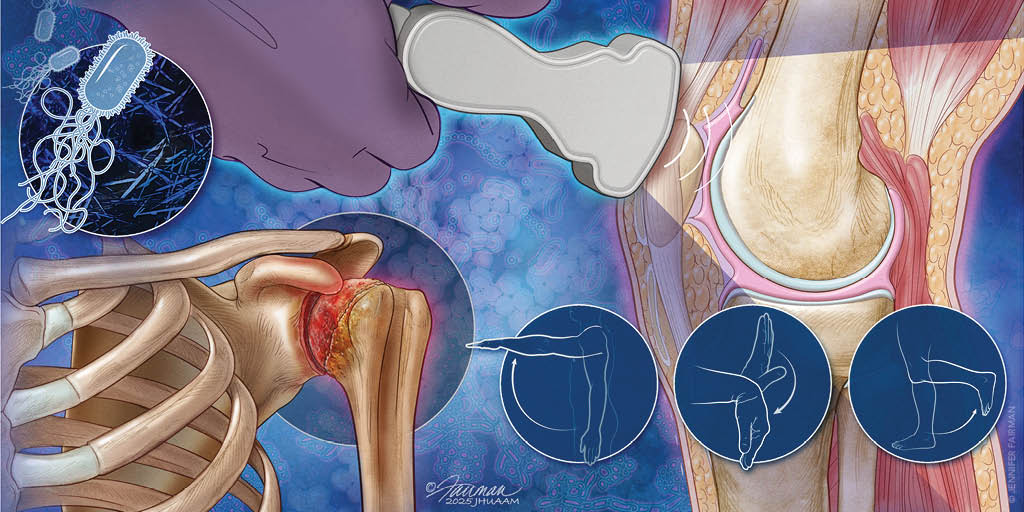
Acute monoarthritis, characterized by pain or swelling in a single joint, is a diagnostic challenge in the primary care setting. Intra-articular conditions typically manifest with reduced active and passive range of motion, whereas patients with periarticular conditions such as tendinitis or bursitis often maintain passive range of motion. When evaluating a patient with acute monoarthritis, it is essential to remember that many polyarthritic processes can initially present in a single joint. A broad differential diagnosis for monoarthritis should include septic arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, trauma, and Lyme arthritis. Of these, septic arthritis is the most urgent and requires prompt intervention. Bacterial culture of the synovial fluid is the most accurate diagnostic test for a septic joint. However, diagnostic accuracy can be increased in the short term by evaluating additional markers such as synovial white blood cell count, synovial lactate, and serum biomarkers. These supplementary tests aid in early decision-making while awaiting bacterial culture results. Osteoarthritis is often clinically diagnosed and may be confirmed with radiography. Gout, the most prevalent crystalline arthropathy, can be diagnosed using specialized calculators, ultrasonography, and dual energy computed tomography. Gout is typically most painful at night or in the early morning. Ultrasonography is useful for identifying effusions in less-visible joints and facilitating precise joint aspiration.
Bing
Acute Monoarthritis: Diagnosis in Adults
Acute monoarthritis, characterized by pain or swelling in a single joint, is a diagnostic challenge in the primary care setting. Intra-articular conditions typically manifest with reduced active and passive range of motion, whereas patients with periarticular conditions such as tendinitis or bursitis often maintain passive range of motion. When evaluating a patient with acute monoarthritis, it is essential to remember that many polyarthritic processes can initially present in a single joint. A broad differential diagnosis for monoarthritis should include septic arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, trauma, and Lyme arthritis. Of these, septic arthritis is the most urgent and requires prompt intervention. Bacterial culture of the synovial fluid is the most accurate diagnostic test for a septic joint. However, diagnostic accuracy can be increased in the short term by evaluating additional markers such as synovial white blood cell count, synovial lactate, and serum biomarkers. These supplementary tests aid in early decision-making while awaiting bacterial culture results. Osteoarthritis is often clinically diagnosed and may be confirmed with radiography. Gout, the most prevalent crystalline arthropathy, can be diagnosed using specialized calculators, ultrasonography, and dual energy computed tomography. Gout is typically most painful at night or in the early morning. Ultrasonography is useful for identifying effusions in less-visible joints and facilitating precise joint aspiration.
DuckDuckGo
Acute Monoarthritis: Diagnosis in Adults
Acute monoarthritis, characterized by pain or swelling in a single joint, is a diagnostic challenge in the primary care setting. Intra-articular conditions typically manifest with reduced active and passive range of motion, whereas patients with periarticular conditions such as tendinitis or bursitis often maintain passive range of motion. When evaluating a patient with acute monoarthritis, it is essential to remember that many polyarthritic processes can initially present in a single joint. A broad differential diagnosis for monoarthritis should include septic arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, trauma, and Lyme arthritis. Of these, septic arthritis is the most urgent and requires prompt intervention. Bacterial culture of the synovial fluid is the most accurate diagnostic test for a septic joint. However, diagnostic accuracy can be increased in the short term by evaluating additional markers such as synovial white blood cell count, synovial lactate, and serum biomarkers. These supplementary tests aid in early decision-making while awaiting bacterial culture results. Osteoarthritis is often clinically diagnosed and may be confirmed with radiography. Gout, the most prevalent crystalline arthropathy, can be diagnosed using specialized calculators, ultrasonography, and dual energy computed tomography. Gout is typically most painful at night or in the early morning. Ultrasonography is useful for identifying effusions in less-visible joints and facilitating precise joint aspiration.
General Meta Tags
33- titleAcute Monoarthritis: Diagnosis in Adults | AAFP
- charsetUTF-8
- descriptionAcute monoarthritis, characterized by pain or swelling in a single joint, is a diagnostic challenge in the primary care setting. Intra-articular conditions typically manifest with reduced active and passive range of motion, whereas patients with periarticular conditions such as tendinitis or bursitis often maintain passive range of motion. When evaluating a patient with acute monoarthritis, it is essential to remember that many polyarthritic processes can initially present in a single joint. A broad differential diagnosis for monoarthritis should include septic arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, trauma, and Lyme arthritis. Of these, septic arthritis is the most urgent and requires prompt intervention. Bacterial culture of the synovial fluid is the most accurate diagnostic test for a septic joint. However, diagnostic accuracy can be increased in the short term by evaluating additional markers such as synovial white blood cell count, synovial lactate, and serum biomarkers. These supplementary tests aid in early decision-making while awaiting bacterial culture results. Osteoarthritis is often clinically diagnosed and may be confirmed with radiography. Gout, the most prevalent crystalline arthropathy, can be diagnosed using specialized calculators, ultrasonography, and dual energy computed tomography. Gout is typically most painful at night or in the early morning. Ultrasonography is useful for identifying effusions in less-visible joints and facilitating precise joint aspiration.
- templateaafp-article-page
- tagsaafp:publications/afp/article-types/feature,aafp:taxonomy/afp/arthritis-and-joint-pain,aafp:publications/afp/topics/arthritis-and-joint-pain/screening-and-diagnosis,aafp:publications/filters/discipline/orthopedic,aafp:publications/filters/discipline/rheumatologic,aafp:publications/filters/population/adults,aafp:publications/filters/content-focus/screening-and-diagnosis
Open Graph Meta Tags
6- og:titleAcute Monoarthritis: Diagnosis in Adults
- og:descriptionAcute monoarthritis, characterized by pain or swelling in a single joint, is a diagnostic challenge in the primary care setting. Intra-articular conditions typically manifest with reduced active and passive range of motion, whereas patients with periarticular conditions such as tendinitis or bursitis often maintain passive range of motion. When evaluating a patient with acute monoarthritis, it is essential to remember that many polyarthritic processes can initially present in a single joint. A broad differential diagnosis for monoarthritis should include septic arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, trauma, and Lyme arthritis. Of these, septic arthritis is the most urgent and requires prompt intervention. Bacterial culture of the synovial fluid is the most accurate diagnostic test for a septic joint. However, diagnostic accuracy can be increased in the short term by evaluating additional markers such as synovial white blood cell count, synovial lactate, and serum biomarkers. These supplementary tests aid in early decision-making while awaiting bacterial culture results. Osteoarthritis is often clinically diagnosed and may be confirmed with radiography. Gout, the most prevalent crystalline arthropathy, can be diagnosed using specialized calculators, ultrasonography, and dual energy computed tomography. Gout is typically most painful at night or in the early morning. Ultrasonography is useful for identifying effusions in less-visible joints and facilitating precise joint aspiration.
- og:imagehttps://www.aafp.org/dam/brand/aafp/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0600/swisher.jpg
- og:image:altAAFP logo in blue with orange flame in torch
- og:urlhttps://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0600/acute-monoarthritis.html
Twitter Meta Tags
6- twitter:cardsummary_large_image
- twitter:site@aafp
- twitter:titleAcute Monoarthritis: Diagnosis in Adults
- twitter:descriptionAcute monoarthritis, characterized by pain or swelling in a single joint, is a diagnostic challenge in the primary care setting. Intra-articular conditions typically manifest with reduced active and passive range of motion, whereas patients with periarticular conditions such as tendinitis or bursitis often maintain passive range of motion. When evaluating a patient with acute monoarthritis, it is essential to remember that many polyarthritic processes can initially present in a single joint. A broad differential diagnosis for monoarthritis should include septic arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, trauma, and Lyme arthritis. Of these, septic arthritis is the most urgent and requires prompt intervention. Bacterial culture of the synovial fluid is the most accurate diagnostic test for a septic joint. However, diagnostic accuracy can be increased in the short term by evaluating additional markers such as synovial white blood cell count, synovial lactate, and serum biomarkers. These supplementary tests aid in early decision-making while awaiting bacterial culture results. Osteoarthritis is often clinically diagnosed and may be confirmed with radiography. Gout, the most prevalent crystalline arthropathy, can be diagnosed using specialized calculators, ultrasonography, and dual energy computed tomography. Gout is typically most painful at night or in the early morning. Ultrasonography is useful for identifying effusions in less-visible joints and facilitating precise joint aspiration.
- twitter:imagehttps://www.aafp.org/dam/brand/aafp/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0600/swisher.jpg
Link Tags
25- canonicalhttps://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0600/acute-monoarthritis.html
- preconnecthttps://ssl.aafp.org
- preconnecthttps://img.aafp.net
- preconnecthttps://css.aafp.net
- preconnecthttps://js.aafp.net
Links
5- https://www.aafp.org/about/this-site/permissions.html
- https://www.aafp.org/cgi-bin/lg.pl?redirect=https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0600/acute-monoarthritis.html
- https://www.aafp.org/membership.html
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0600.html
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/subscribe.html