www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0700/fingertip-injuries.html
Preview meta tags from the www.aafp.org website.
Linked Hostnames
1Thumbnail
Search Engine Appearance
Fingertip Injuries
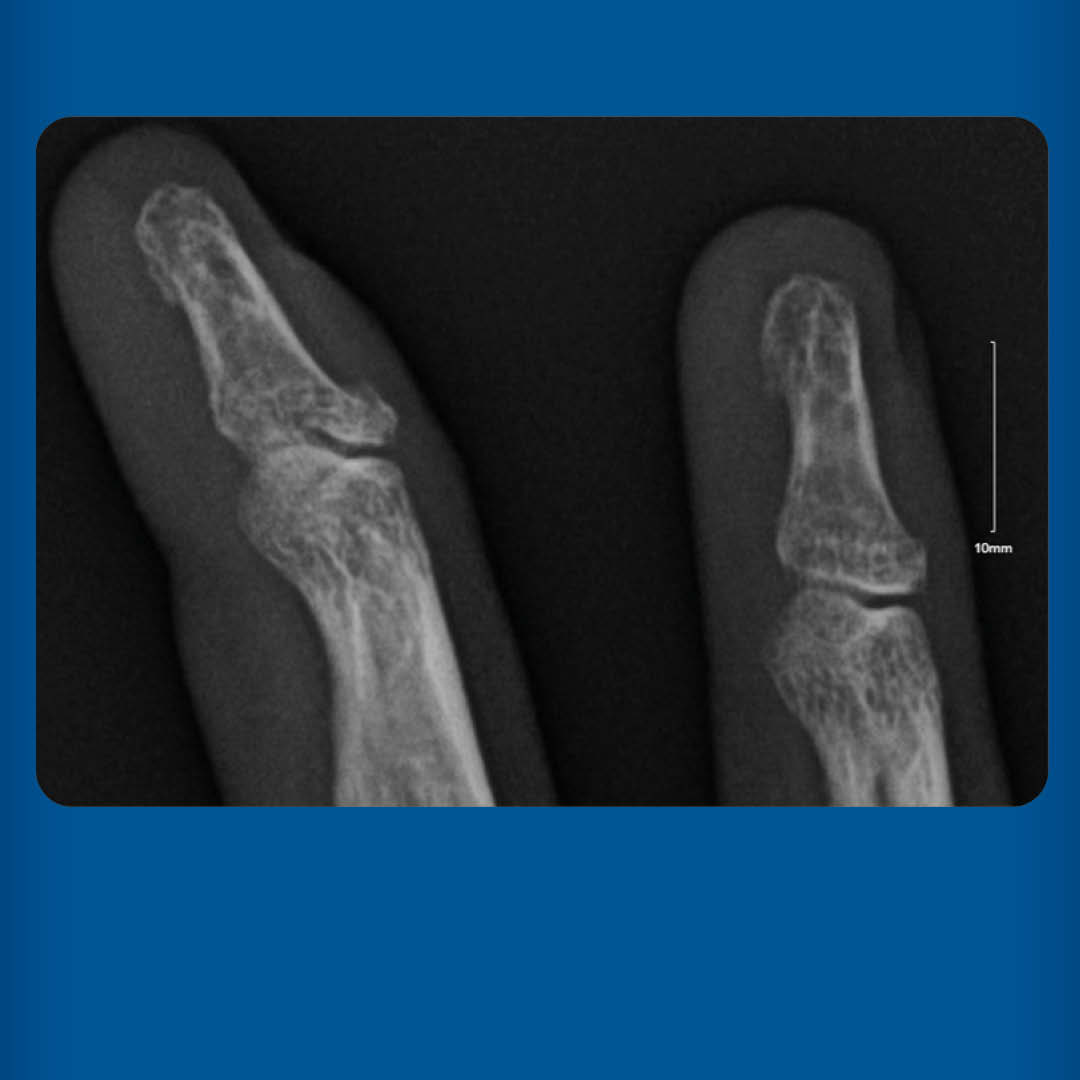
Family physicians play a pivotal role in providing timely care for common fingertip injuries and minimizing long-term disability after injury. Subungual hematoma is diagnosed clinically and treated with observation or nail trephination. Nail bed lacerations are treated by removal of the nail and repair of the nail bed. Distal interphalangeal joint dislocations typically occur dorsally and result from hyperextension or hyperflexion during sports or because of accidental trauma. Management primarily involves closed reduction and splinting; however, surgical intervention might be necessary for complex cases. Distal phalanx fractures are most often minimally displaced and amenable to closed reduction and splinting; open and intra-articular fractures involving more than one-third of the articular surface require referral to a hand surgeon. Mallet finger comprises rupture of the extensor digitorum tendon or avulsion from the adjacent distal phalanx, inhibiting distal interphalangeal joint extension, and typically heals after 6 to 8 weeks of constant immobilization. Jersey finger involves similar injuries to the flexor digitorum profundus tendon but necessitates referral for surgical repair to restore function.
Bing
Fingertip Injuries
Family physicians play a pivotal role in providing timely care for common fingertip injuries and minimizing long-term disability after injury. Subungual hematoma is diagnosed clinically and treated with observation or nail trephination. Nail bed lacerations are treated by removal of the nail and repair of the nail bed. Distal interphalangeal joint dislocations typically occur dorsally and result from hyperextension or hyperflexion during sports or because of accidental trauma. Management primarily involves closed reduction and splinting; however, surgical intervention might be necessary for complex cases. Distal phalanx fractures are most often minimally displaced and amenable to closed reduction and splinting; open and intra-articular fractures involving more than one-third of the articular surface require referral to a hand surgeon. Mallet finger comprises rupture of the extensor digitorum tendon or avulsion from the adjacent distal phalanx, inhibiting distal interphalangeal joint extension, and typically heals after 6 to 8 weeks of constant immobilization. Jersey finger involves similar injuries to the flexor digitorum profundus tendon but necessitates referral for surgical repair to restore function.
DuckDuckGo
Fingertip Injuries
Family physicians play a pivotal role in providing timely care for common fingertip injuries and minimizing long-term disability after injury. Subungual hematoma is diagnosed clinically and treated with observation or nail trephination. Nail bed lacerations are treated by removal of the nail and repair of the nail bed. Distal interphalangeal joint dislocations typically occur dorsally and result from hyperextension or hyperflexion during sports or because of accidental trauma. Management primarily involves closed reduction and splinting; however, surgical intervention might be necessary for complex cases. Distal phalanx fractures are most often minimally displaced and amenable to closed reduction and splinting; open and intra-articular fractures involving more than one-third of the articular surface require referral to a hand surgeon. Mallet finger comprises rupture of the extensor digitorum tendon or avulsion from the adjacent distal phalanx, inhibiting distal interphalangeal joint extension, and typically heals after 6 to 8 weeks of constant immobilization. Jersey finger involves similar injuries to the flexor digitorum profundus tendon but necessitates referral for surgical repair to restore function.
General Meta Tags
31- titleFingertip Injuries | AAFP
- charsetUTF-8
- descriptionFamily physicians play a pivotal role in providing timely care for common fingertip injuries and minimizing long-term disability after injury. Subungual hematoma is diagnosed clinically and treated with observation or nail trephination. Nail bed lacerations are treated by removal of the nail and repair of the nail bed. Distal interphalangeal joint dislocations typically occur dorsally and result from hyperextension or hyperflexion during sports or because of accidental trauma. Management primarily involves closed reduction and splinting; however, surgical intervention might be necessary for complex cases. Distal phalanx fractures are most often minimally displaced and amenable to closed reduction and splinting; open and intra-articular fractures involving more than one-third of the articular surface require referral to a hand surgeon. Mallet finger comprises rupture of the extensor digitorum tendon or avulsion from the adjacent distal phalanx, inhibiting distal interphalangeal joint extension, and typically heals after 6 to 8 weeks of constant immobilization. Jersey finger involves similar injuries to the flexor digitorum profundus tendon but necessitates referral for surgical repair to restore function.
- templateaafp-article-page
- tagsaafp:publications/afp/article-types/feature,aafp:publications/afp/topics/musculoskeletal-care/wrist-and-hand,aafp:publications/filters/discipline/orthopedic,aafp:publications/filters/content-focus/treatment,aafp:taxonomy/afp/nail-disorders,aafp:taxonomy/afp/hand%2C-finger%2C-and-wrist-disorders,aafp:taxonomy/afp/fractures
Open Graph Meta Tags
6- og:titleFingertip Injuries
- og:descriptionFamily physicians play a pivotal role in providing timely care for common fingertip injuries and minimizing long-term disability after injury. Subungual hematoma is diagnosed clinically and treated with observation or nail trephination. Nail bed lacerations are treated by removal of the nail and repair of the nail bed. Distal interphalangeal joint dislocations typically occur dorsally and result from hyperextension or hyperflexion during sports or because of accidental trauma. Management primarily involves closed reduction and splinting; however, surgical intervention might be necessary for complex cases. Distal phalanx fractures are most often minimally displaced and amenable to closed reduction and splinting; open and intra-articular fractures involving more than one-third of the articular surface require referral to a hand surgeon. Mallet finger comprises rupture of the extensor digitorum tendon or avulsion from the adjacent distal phalanx, inhibiting distal interphalangeal joint extension, and typically heals after 6 to 8 weeks of constant immobilization. Jersey finger involves similar injuries to the flexor digitorum profundus tendon but necessitates referral for surgical repair to restore function.
- og:imagehttps://www.aafp.org/dam/brand/aafp/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0700/becker.jpg
- og:image:altAAFP logo in blue with orange flame in torch
- og:urlhttps://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0700/fingertip-injuries.html
Twitter Meta Tags
6- twitter:cardsummary_large_image
- twitter:site@aafp
- twitter:titleFingertip Injuries
- twitter:descriptionFamily physicians play a pivotal role in providing timely care for common fingertip injuries and minimizing long-term disability after injury. Subungual hematoma is diagnosed clinically and treated with observation or nail trephination. Nail bed lacerations are treated by removal of the nail and repair of the nail bed. Distal interphalangeal joint dislocations typically occur dorsally and result from hyperextension or hyperflexion during sports or because of accidental trauma. Management primarily involves closed reduction and splinting; however, surgical intervention might be necessary for complex cases. Distal phalanx fractures are most often minimally displaced and amenable to closed reduction and splinting; open and intra-articular fractures involving more than one-third of the articular surface require referral to a hand surgeon. Mallet finger comprises rupture of the extensor digitorum tendon or avulsion from the adjacent distal phalanx, inhibiting distal interphalangeal joint extension, and typically heals after 6 to 8 weeks of constant immobilization. Jersey finger involves similar injuries to the flexor digitorum profundus tendon but necessitates referral for surgical repair to restore function.
- twitter:imagehttps://www.aafp.org/dam/brand/aafp/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0700/becker.jpg
Link Tags
25- canonicalhttps://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0700/fingertip-injuries.html
- preconnecthttps://ssl.aafp.org
- preconnecthttps://img.aafp.net
- preconnecthttps://css.aafp.net
- preconnecthttps://js.aafp.net
Links
5- https://www.aafp.org/about/this-site/permissions.html
- https://www.aafp.org/cgi-bin/lg.pl?redirect=https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0700/fingertip-injuries.html
- https://www.aafp.org/membership.html
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2025/0700.html
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/subscribe.html