www.nature.com/ng/journal/v47/n9/full/ng.3367.html
Preview meta tags from the www.nature.com website.
Linked Hostnames
29- 114 links towww.nature.com
- 88 links towww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- 45 links todoi.org
- 44 links toscholar.google.com
- 11 links toscholar.google.co.uk
- 8 links towww.springernature.com
- 4 links topartnerships.nature.com
- 3 links toauthorservices.springernature.com
Thumbnail
Search Engine Appearance
A gene-based association method for mapping traits using reference transcriptome data - Nature Genetics
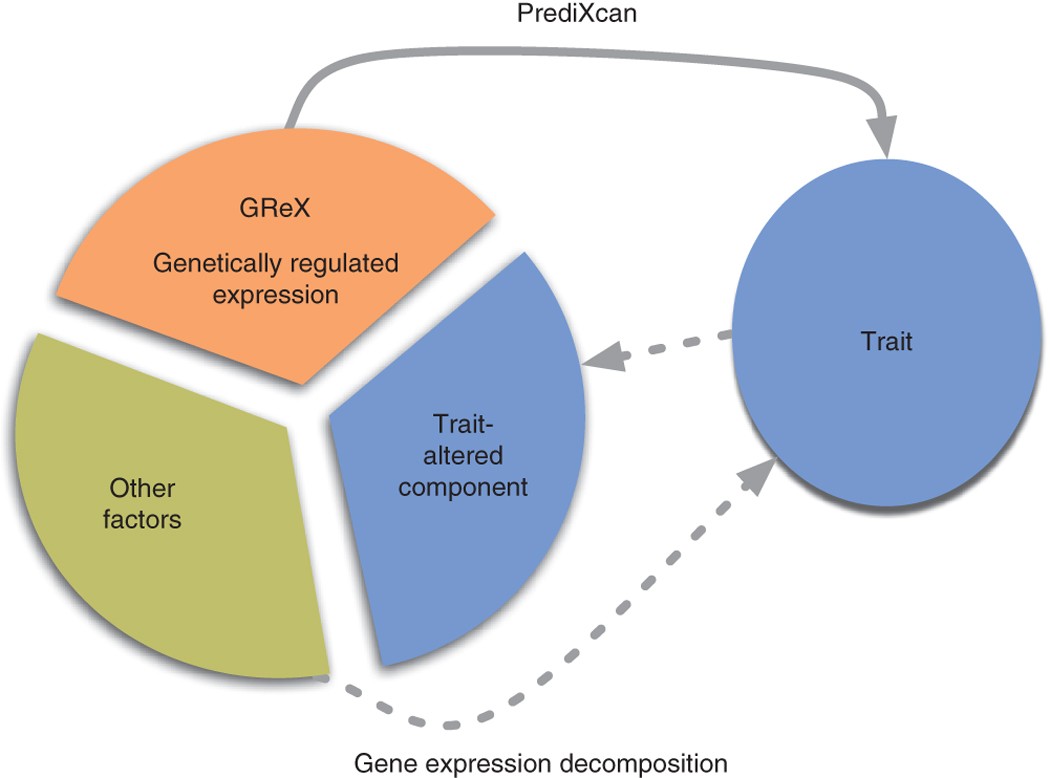
Hae Kyung Im and colleagues report a method for predicting gene expression perturbations from genotype data after training on reference transcriptome data sets. Association of predicted gene expression with disease traits identifies known and new candidate disease genes. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified thousands of variants robustly associated with complex traits. However, the biological mechanisms underlying these associations are, in general, not well understood. We propose a gene-based association method called PrediXcan that directly tests the molecular mechanisms through which genetic variation affects phenotype. The approach estimates the component of gene expression determined by an individual's genetic profile and correlates 'imputed' gene expression with the phenotype under investigation to identify genes involved in the etiology of the phenotype. Genetically regulated gene expression is estimated using whole-genome tissue-dependent prediction models trained with reference transcriptome data sets. PrediXcan enjoys the benefits of gene-based approaches such as reduced multiple-testing burden and a principled approach to the design of follow-up experiments. Our results demonstrate that PrediXcan can detect known and new genes associated with disease traits and provide insights into the mechanism of these associations.
Bing
A gene-based association method for mapping traits using reference transcriptome data - Nature Genetics
Hae Kyung Im and colleagues report a method for predicting gene expression perturbations from genotype data after training on reference transcriptome data sets. Association of predicted gene expression with disease traits identifies known and new candidate disease genes. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified thousands of variants robustly associated with complex traits. However, the biological mechanisms underlying these associations are, in general, not well understood. We propose a gene-based association method called PrediXcan that directly tests the molecular mechanisms through which genetic variation affects phenotype. The approach estimates the component of gene expression determined by an individual's genetic profile and correlates 'imputed' gene expression with the phenotype under investigation to identify genes involved in the etiology of the phenotype. Genetically regulated gene expression is estimated using whole-genome tissue-dependent prediction models trained with reference transcriptome data sets. PrediXcan enjoys the benefits of gene-based approaches such as reduced multiple-testing burden and a principled approach to the design of follow-up experiments. Our results demonstrate that PrediXcan can detect known and new genes associated with disease traits and provide insights into the mechanism of these associations.
DuckDuckGo
A gene-based association method for mapping traits using reference transcriptome data - Nature Genetics
Hae Kyung Im and colleagues report a method for predicting gene expression perturbations from genotype data after training on reference transcriptome data sets. Association of predicted gene expression with disease traits identifies known and new candidate disease genes. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified thousands of variants robustly associated with complex traits. However, the biological mechanisms underlying these associations are, in general, not well understood. We propose a gene-based association method called PrediXcan that directly tests the molecular mechanisms through which genetic variation affects phenotype. The approach estimates the component of gene expression determined by an individual's genetic profile and correlates 'imputed' gene expression with the phenotype under investigation to identify genes involved in the etiology of the phenotype. Genetically regulated gene expression is estimated using whole-genome tissue-dependent prediction models trained with reference transcriptome data sets. PrediXcan enjoys the benefits of gene-based approaches such as reduced multiple-testing burden and a principled approach to the design of follow-up experiments. Our results demonstrate that PrediXcan can detect known and new genes associated with disease traits and provide insights into the mechanism of these associations.
General Meta Tags
153- titleA gene-based association method for mapping traits using reference transcriptome data | Nature Genetics
- titleClose banner
- titleClose banner
- X-UA-CompatibleIE=edge
- applicable-devicepc,mobile
Open Graph Meta Tags
6- og:urlhttps://www.nature.com/articles/ng.3367
- og:typearticle
- og:site_nameNature
- og:titleA gene-based association method for mapping traits using reference transcriptome data - Nature Genetics
- og:descriptionHae Kyung Im and colleagues report a method for predicting gene expression perturbations from genotype data after training on reference transcriptome data sets. Association of predicted gene expression with disease traits identifies known and new candidate disease genes.
Twitter Meta Tags
6- twitter:site@NatureGenet
- twitter:cardsummary_large_image
- twitter:image:altContent cover image
- twitter:titleA gene-based association method for mapping traits using reference transcriptome data
- twitter:descriptionNature Genetics - Hae Kyung Im and colleagues report a method for predicting gene expression perturbations from genotype data after training on reference transcriptome data sets. Association of...
Item Prop Meta Tags
5- position1
- position2
- position3
- position4
- publisherSpringer Nature
Link Tags
15- alternatehttps://www.nature.com/ng.rss
- apple-touch-icon/static/images/favicons/nature/apple-touch-icon-f39cb19454.png
- canonicalhttps://www.nature.com/articles/ng.3367
- icon/static/images/favicons/nature/favicon-48x48-b52890008c.png
- icon/static/images/favicons/nature/favicon-32x32-3fe59ece92.png
Emails
1Links
345- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=A%20novel%20susceptibility%20locus%20for%20type%201%20diabetes%20on%20Chr12q13%20identified%20by%20a%20genome-wide%20association%20study&journal=Diabetes&doi=10.2337%2Fdb07-1305&volume=57&pages=1143-1146&publication_year=2008&author=Hakonarson%2CH
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=A%20versatile%20gene-based%20test%20for%20genome-wide%20association%20studies&journal=Am.%20J.%20Hum.%20Genet.&doi=10.1016%2Fj.ajhg.2010.06.009&volume=87&pages=139-145&publication_year=2010&author=Liu%2CJZ
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=Association%20analyses%20of%20249%2C796%20individuals%20reveal%2018%20new%20loci%20associated%20with%20body%20mass%20index&journal=Nat.%20Genet.&doi=10.1038%2Fng.686&volume=42&pages=937-948&publication_year=2010&author=Speliotes%2CEK
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=Characterizing%20the%20genetic%20basis%20of%20transcriptome%20diversity%20through%20RNA-sequencing%20of%20922%20individuals&journal=Genome%20Res.&doi=10.1101%2Fgr.155192.113&volume=24&pages=14-24&publication_year=2014&author=Battle%2CA
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=Chemotherapeutic%20drug%20susceptibility%20associated%20SNPs%20are%20enriched%20in%20expression%20quantitative%20trait%20loci&journal=Proc.%20Natl.%20Acad.%20Sci.%20USA&doi=10.1073%2Fpnas.1001827107&volume=107&pages=9287-9292&publication_year=2010&author=Gamazon%2CER&author=Huang%2CRS&author=Cox%2CNJ&author=Dolan%2CME